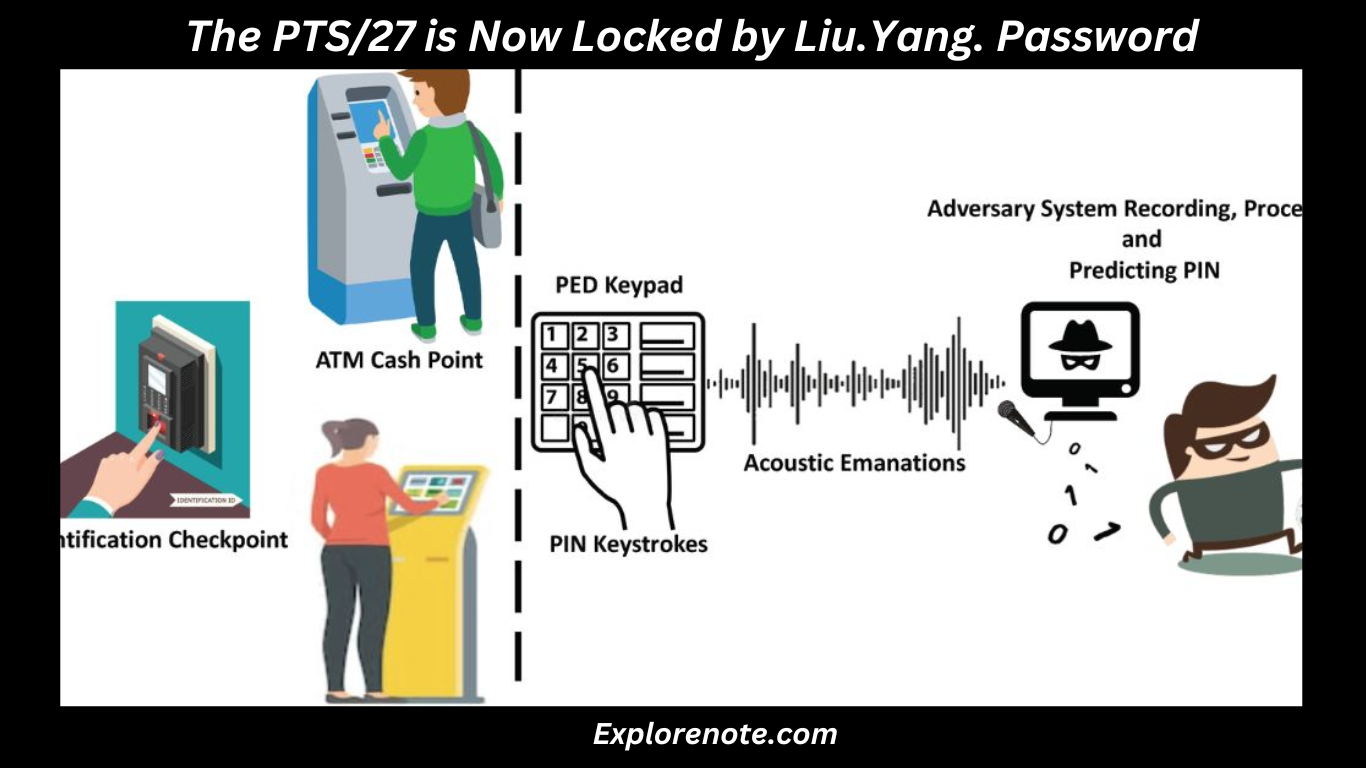
In today’s digital landscape, password security is paramount. One common issue many users face is being locked out of their accounts due to authentication failures.
A recent example illustrates this issue well: The PTS/27 is now locked by Liu.Yang. Password: Authentication Failure.
This situation raises questions about security measures, user experiences, and the implications of password management.
In this article, we will delve into the specifics of this lockout message, explore related terms, and offer insights on how to navigate such issues effectively.
Understanding the Lockout Message
When encountering the message “The PTS/27 is now locked by Liu.Yang. Password: Authentication Failure,” it indicates that an account or system, referred to as PTS/27, has been secured by a user named Liu.Yang.
The additional detail about a password authentication failure suggests that there were multiple incorrect password attempts.
What Causes Authentication Failures?
Authentication failures typically occur due to one of the following reasons:
- Incorrect Password Entry: Users might mistakenly input the wrong password. This is the most common cause.
- Caps Lock or Num Lock: Often, users forget that these keys are enabled, resulting in incorrect character inputs.
- Expired Passwords: Some systems enforce password expiration policies, requiring users to update their passwords periodically.
- Account Lockout Policies: Many organizations implement security measures that temporarily lock accounts after a set number of failed login attempts to prevent unauthorized access.
- System Errors: Occasionally, bugs or glitches within the authentication system can lead to false authentication failures.
Also Read: Unlock the Full Potential of Lost Ark with Lostarkbr com – Your Ultimate Gaming Companion
The Implications of Being Locked Out
Being locked out of an account can have various implications, especially in professional or sensitive environments. Here are some potential consequences:
1. Access Disruption
Being locked out means you cannot access essential tools or data. For individuals working in IT or sensitive environments, this could lead to significant productivity losses.
2. Increased Frustration
Repeated failures can lead to frustration, impacting the user’s overall experience and relationship with the platform or service.
3. Security Concerns
Repeated lockouts may signal attempts by unauthorized users to access an account, raising alarms about potential security breaches.

4. Recovery Processes
Recovering a locked account often requires additional steps, including answering security questions, waiting for administrative approval, or receiving recovery emails.
This process can be time-consuming and cumbersome.
Analyzing Password Management Strategies
Given the prevalence of authentication failures, it’s crucial to implement effective password management strategies.
Here are some tips to help mitigate the risks associated with password-related issues:
1. Use Password Managers
Password managers can generate and store complex passwords, reducing the likelihood of password-related lockouts.
They also facilitate secure sharing of passwords among team members.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra layer of security. Even if a password is compromised, the account remains secure without the second authentication factor.
3. Regularly Update Passwords
Adopting a routine for updating passwords can enhance security. It’s advisable to change passwords every three to six months.
Also Read: Unlock Big Savings with LookWhatMomFound.com Codes_ The Ultimate Guide for Smart Shoppers
4. Create Strong Passwords
Strong passwords typically consist of at least 12 characters, incorporating a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols.
5. Educate Users
Organizations should invest in educating users about the importance of password security and the implications of authentication failures. Regular training can significantly reduce mistakes.
Related Terms to Consider
Understanding “The PTS/27 is now locked by Liu.Yang. Password: Authentication Failure” also involves recognizing several related terms that are essential in the realm of cybersecurity and account management.
1. Account Lockout Policy
An account lockout policy is a security measure that limits the number of failed login attempts before an account is temporarily locked.
This policy helps deter unauthorized access but can lead to user frustration if not managed properly.
2. Password Reset
A password reset process enables users to regain access to their accounts after being locked out.
This typically involves verifying the user’s identity through email or SMS.
3. Authentication Protocols
Authentication protocols are methods used to verify a user’s identity before granting access to a system. Common protocols include OAuth, SAML, and OpenID Connect.
4. Brute Force Attack
A brute force attack occurs when a malicious actor systematically attempts various password combinations to gain unauthorized access to an account.
This tactic is often the reason behind multiple authentication failures.
Personal Insights and Interpretations
Lockouts such as “The PTS/27 is now locked by Liu.Yang. Password: Authentication Failure” emphasize the necessity for robust security protocols.
The incident illustrates how easily users can become locked out, not merely from negligence but also due to the increasing complexity of security measures.
Also Read: Phaelonthilyx_ The Bold New Voice in Parenting and Lifestyle Blogging
Enhancing User Experience
To minimize the frustration associated with authentication failures, companies should consider the following:
- Streamlined Recovery Processes: Simplifying the steps to recover access to accounts can alleviate stress for users who may feel overwhelmed after repeated failures.
- User-Centric Design: Ensuring that user interfaces are intuitive and guide users through authentication processes can reduce errors significantly.
- Transparent Communication: Companies should communicate clearly when lockout policies are enforced, helping users understand the rationale behind security measures.
Building a Culture of Security Awareness
Organizations must foster a culture that values security. Encouraging employees to share their experiences with lockouts can lead to collective learning and improved practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What should I do if I see the lockout message?
If you encounter the message “The PTS/27 is now locked by Liu.Yang. Password: Authentication Failure,” try to remember your password and enter it again carefully.
If you still can’t access your account, follow the password reset procedures or contact your system administrator.
How can I avoid being locked out of my account?
To prevent lockouts, use a password manager, enable two-factor authentication, regularly update your passwords, and avoid using easily guessable passwords.
Is it safe to use the same password across multiple accounts?
No, using the same password across multiple accounts increases the risk of being locked out if one account is compromised. Always use unique passwords for each account.
What are the common signs of a potential security breach?
Common signs include unexpected lockouts, unfamiliar account activity, receiving password reset emails you did not request, or unusual alerts from your security software.
How often should I change my password?
It’s advisable to change your passwords every three to six months or immediately if you suspect that your account may have been compromised.
Conclusion
The message “The PTS/27 is now locked by Liu.Yang. Password: Authentication Failure” serves as a reminder of the importance of password security in today’s digital world.
By understanding the causes of authentication failures, implementing effective password management strategies, and fostering a culture of security awareness, individuals and organizations can navigate the complexities of digital security with confidence.
Remember, proactive measures are always better than reactive ones. Stay informed, stay secure, and ensure that your digital interactions remain safe and productive.
Also Read: Give aways Look What Mom Found – A Fun World of Freebies and Family Finds